What are Cross Border Payments?
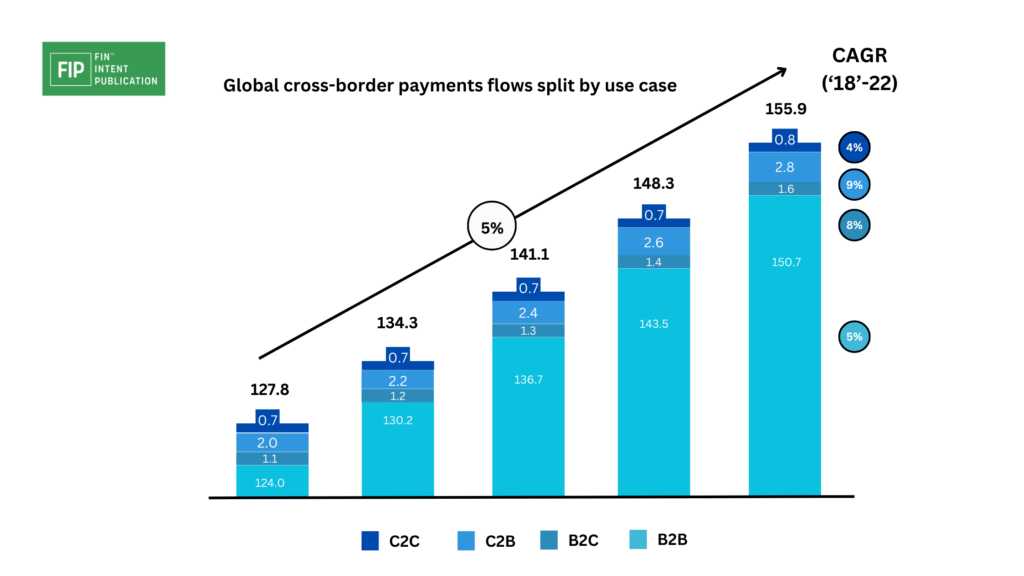
Cross-border payments refer to transactions involving banks, financial institutions, businesses, or individuals located in different countries, regardless of whether they share a common border. Projections from a Juniper Research report indicate that cross-border B2B payments are anticipated to surpass $40 trillion globally by 2024, experiencing growth from $37 trillion in 2022.
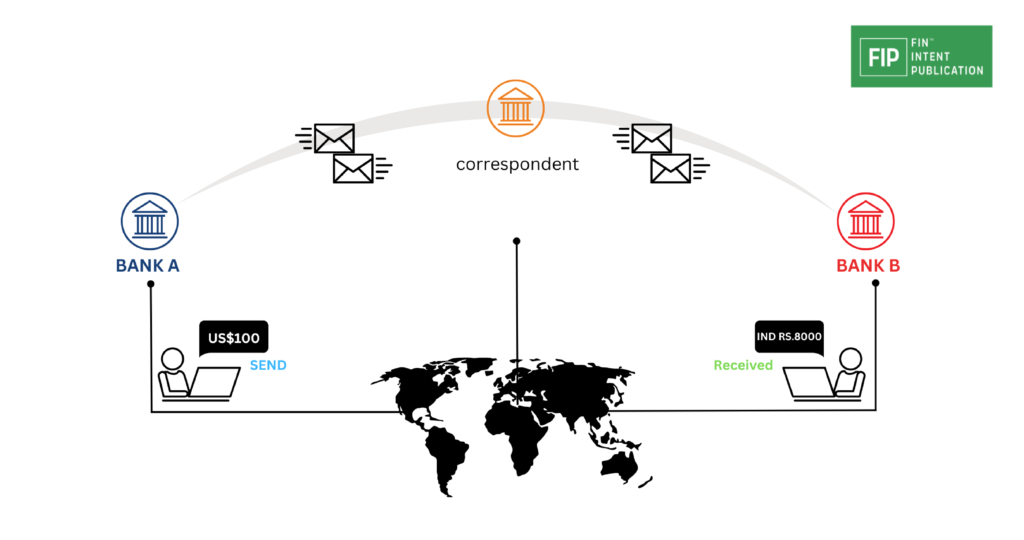
Who Uses Cross-Border Payments?
The utilization of cross-border payments is widespread, encompassing diverse entities worldwide. Tipalti’s original findings, available on an interactive map, showcase each country’s preferred method for cross-border payments. The map allows users to explore results based on payment size range, apply filters, or hover over a specific country for detailed insights.
Types of cross-border payments
Cross-border payments involve the seamless transfer of funds between entities in different countries. Selecting global payment platforms that support multiple payment options ensures compatibility with various currencies, exchange rates, and more.
1. International Wire Transfers
International wire transfers, a prevalent method for cross-border transactions, involve the sender providing detailed instructions to their bank for the secure transfer of funds to a recipient in another country. The active participation of banks plays a crucial role in facilitating the movement of funds across borders. This intricate process is made secure through the utilization of internationally recognized codes such as IBAN & SWIFT, ensuring a reliable and traceable transfer between banks in different countries. The incorporation of these codes enhances the security and efficiency of international wire transfers.
2. Global ACH Payments
Global ACH (Automated Clearing House) payments, an electronic means for fund transfers between bank accounts within the United States, are renowned for their efficiency. This method boasts completion times of 1-2 business days, providing a swift and reliable avenue for cross-border transactions. Global ACH payments support a diverse range of transaction types, including direct deposits, electronic bill payments, and point-of-sale (POS) transactions, contributing to its versatility and widespread adoption within the financial landscape.
3. Digital Wallets
Digital wallets, epitomized by popular products such as PayPal, Google Pay, or Apple Pay, serve as dynamic cross-border payment solutions. While they excel in facilitating convenient individual or peer-to-peer transactions, digital wallets may not be the ideal choice for substantial transfers due to varying transaction fees. Despite this limitation, their seamless integration with everyday transactions and widespread accessibility positions digital wallets as a prominent player in the cross-border payments arena.
4. Credit and Debit Card Payments
Credit and debit card payments stand as universally embraced examples of cross-border transactions, catering to both online and offline purchases on a global scale. Renowned for their convenience, these payment methods, however, may carry associated fees. It is prudent for users to proactively check with their card providers regarding potential transaction charges before initiating cross-border payments. This upfront awareness allows for informed decision-making and ensures a smoother financial transaction experience.
5. Digital Currencies
The emergence and adoption of digital currencies, including prominent ones like Bitcoin, Litecoin, and Ethereum, present an additional dimension to cross-border payments. While offering diverse options, users must exercise caution due to potential issues related to reliability and safety concerns associated with fraudulent activities. The expanding landscape of digital currencies contributes to the evolving dynamics of cross-border financial transactions.
6. Paper Checks
A classic and enduring option for cross-border payments, paper checks continue to be relevant in contemporary financial practices. To utilize paper checks, the sender simply needs to accurately fill in the recipient’s name and address. The absence of fees and intermediary banks in these transactions provides a distinct advantage. However, the drawback lies in the extended processing time, often taking weeks when relying on postal mail. Despite this, paper checks maintain a niche for certain cross-border transactions, combining tradition with practical utility.
Navigating Challenges in Cross-Border Payments
Cross-border payments present several challenges, and being aware of these obstacles, along with implementing effective strategies, is crucial for businesses engaging in international money transfers. Overcoming these challenges empowers companies to conduct transactions confidently and efficiently.
1. High Fees
A significant challenge in cross-border payments is the presence of varied fee structures. For example, when using PayPal for international transactions, users may encounter fees ranging from 3-5%, comprising a fixed fee based on the currency and a percentage of the transaction amount. Banks, on the other hand, typically charge $15-$45 for outgoing international wire transfers and $8-$20 for incoming transfers. International ACH transfers (IAT) also incur fees, albeit generally lower than wire transfers, averaging around $3-$5 per transaction. Awareness of these fees is essential for businesses to optimize their cost management strategies.
2. Time to Clear
The processing time for international payments varies significantly across methods. Wire transfers are relatively fast, typically completed within 1-3 business days, although delays can occur due to factors like time zones, intermediary banks, or processing errors. ACH transfers, employing batch processing, take longer—usually 2-4 business days for international transactions. PayPal offers instant transfers between accounts but may take an additional 1-3 business days when transferring funds to a bank account. Businesses must factor in these time frames to prevent late payments and associated consequences.
3. Foreign Currency Markups
Exchange rate fluctuations and currency conversion markups introduce complexity and additional costs. Banks often apply a 1-3% markup over the mid-market rate, potentially resulting in higher costs than the actual exchange rate. PayPal is known for its high currency conversion fees, typically adding a 3-4% markup over the base exchange rate. Online Transfer Services, like Wise, usually offer rates closer to mid-market values, presenting a more cost-effective option for currency conversion. Businesses must carefully assess these factors to optimize their financial efficiency in cross-border transactions.
Conclusion
This comprehensive exploration sheds light on the intricate world of cross-border payments, emphasizing their significance in the global financial landscape. Understanding the diverse methods, from traditional paper checks to cutting-edge digital currencies, provides businesses with a toolkit for navigating international transactions efficiently.
The escalating trends, as indicated by Juniper Research, underscore the substantial growth expected in cross-border B2B payments, emphasizing the pivotal role these transactions play in the modern economy. The use of global payment platforms accommodating various options ensures adaptability to currencies, exchange rates, and more, contributing to seamless cross-border financial operations.